css sticky检测粘性(position属性的6个取值详解)
前端中position的含义是指定位类型,取值类型可以有:static、relative、absolute、fixed、inherit和sticky这6个属性取值,这里sticky是CSS3新发布的一个属性,sticky检测粘性。
一、static
static 是 position 的默认值,就是没有定位,元素处于现在正常的文档流中
二、relative
relative 是相对定位,指的是给元素设置相对于自己原本位置的定位,元素并不脱离文档流,因此元素原本的位置会被保留,其他的元素位置不会受到影响
案例演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
.container {
width: 100%;
height: 300px;
}
.content {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.content_yellow {
background-color: yellow;
}
.content_red {
background-color: red;
}
.content_black {
background-color: black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div class="content_yellow content"></div>
<div class="content_red content"></div>
<div class="content_black content"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
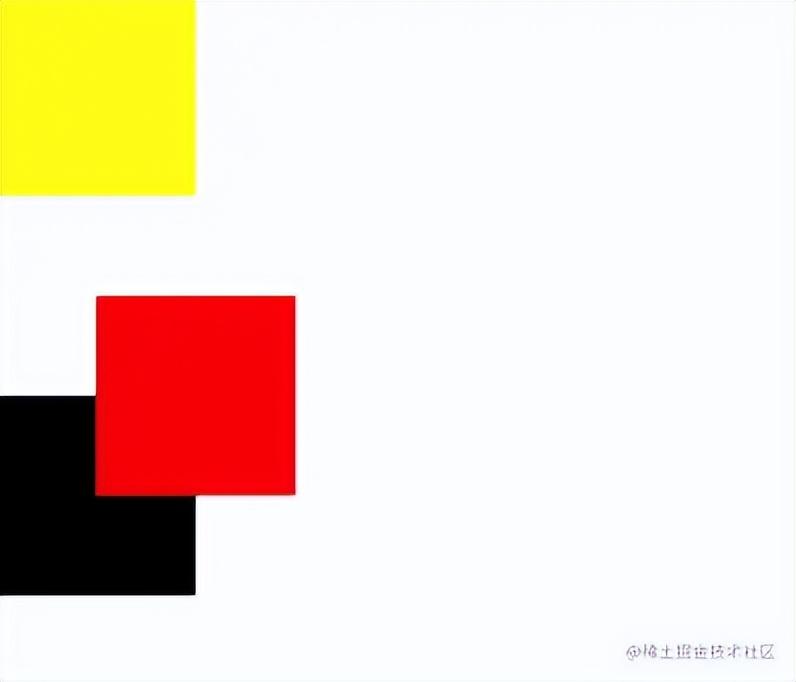
现在给红色方块设置上相对定位,相对于自身向右偏移50px,向下偏移50px
.content_red {
background-color: red;
position: relative;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
三、absolute
absolute 是绝对定位,是的指让元素相对于 static 定位之外的第一个父元素进行定位,分为两种情况
设置了 absolute 的元素如果存在有父元素设置了 position 属性为 relative 或者absolute,此时该元素就以这些父元素来进行定位
如果没有设置了 position 属性为 relative 或者 absolute 父元素,则此时相对于 body 进行定位
absolute 是生成的绝对定位的元素,是会脱离了文本流的,即在文档中已经不占据位置,常用于结合 relative 来使用
<div class="fu">
<div class="son">
子元素
</div>
</div>
.fu {
height: 500px;
width: 500px;
background-color: burlywood;
position: relative;
}
.son {
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
top:50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%,-50%);
}四、fixed
fixed 是一种特殊的绝对定位,也会脱离文档流,只不过 fixed 的元素是固定相对与 body 来定位的
五、sticky
Sticky是CSS3的一个定位属性,它可以让元素在滚动过程中“粘”在屏幕上的某个位置,直到滚动到某个临界点后才会跟随滚动。Sticky定位可以使得页面更具交互性和易用性,也提高了页面的可读性。
sticky 是粘性定位,可以说是相对定位 relative 和固定定位 fixed 的结合体,一开始是没有脱离文档流的,但是当元素距离其父元素的距离达到 sticky 粘性定位的要求时 position:sticky 这时的效果相当于 fixed 定位,固定到适当位置,脱离了文档流。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/* 粘性定位 */
/* 粘性定位可以被认为是相对定位和固定定位的混合。元素在跨越特定值前被认为是相对定位,之后为固定定位 */
*{
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
body{
height: 2000px;
}
div{
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
}
.header{
height: 40px;
width: 100%;
background-color: yellow;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
}
.banner{
height: 80px;
background-color: rosybrown;
margin-top: 40px;
}
.nav{
height: 40px;
background-color: royalblue;
position: sticky;
top:40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
头部
</div>
<div>
banner区域
</div>
<div>
导航栏
</div>
</body>
</html>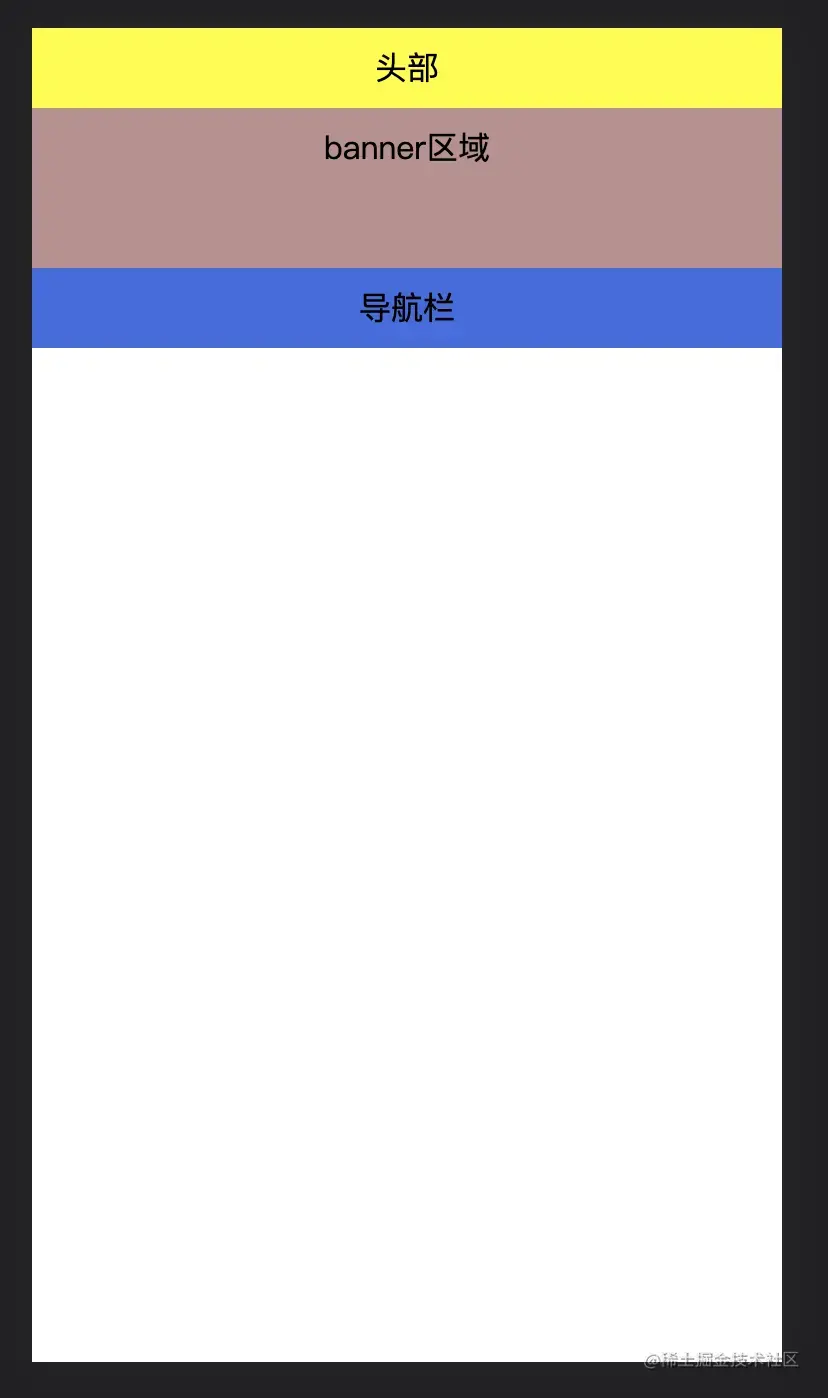
当向下滚动,导航栏具体顶部40px的时候,就会变成固定定位

六、inherit
inherit 就是继承父元素的 position 属性。
原文地址:https://tangjiusheng.cn/divcss/11047.html

